What is HIPAA In Cyber Security?
Welcome to the world of healthcare data protection! In today’s digital age, safeguarding sensitive patient information is more critical than ever. One of the key players in ensuring the security and privacy of this data is HIPAA—the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act. Let’s explore how HIPAA intersects with cybersecurity to protect valuable healthcare information from potential threats.
Relevant Laws and Regulations
Understanding the relevant laws and regulations is crucial for ensuring compliance with HIPAA in cybersecurity. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) sets the standard for protecting sensitive patient data. Additionally, the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act strengthens HIPAA’s privacy and security protections.
Organizations that handle healthcare information must also comply with other regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) if they process data of European Union residents. These laws protect personal health information from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure.
Furthermore, the HIPAA Security Rule requires covered entities and business associates to implement appropriate administrative, physical, and technical safeguards to protect electronic protected health information (ePHI). This includes conducting regular risk assessments, implementing access controls and audit logs, and encrypting ePHI.
In addition to federal laws, healthcare organizations must also comply with state-specific regulations. For example, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) requires organizations that handle the personal information of California residents to implement reasonable security measures and notify individuals in case of a data breach.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Failure to comply with HIPAA and other relevant laws can significantly penalize healthcare organizations. Violations can lead to fines ranging from $100 to $50,000 per violation or per record compromised, up to a maximum of $1.5 million per year. The actual amount of the fine depends on the level of negligence involved.
In addition to financial penalties, non-compliant organizations may face reputational damage and legal action from affected individuals. Therefore, healthcare organizations must take the necessary steps to ensure compliance with all relevant laws and regulations.
Critical Components of HIPAA Cyber Security
Understanding the critical components of HIPAA cyber security is crucial for safeguarding sensitive patient data. One vital aspect is conducting regular risk assessments to identify system vulnerabilities. This proactive approach enables healthcare organizations to address weaknesses before cyber threats exploit them.
Encryption plays a significant role in protecting electronic health information from unauthorized access. Implementing robust encryption methods ensures that data remains secure both at rest and in transit. Access controls are another essential component of HIPAA compliance, as limiting who can view or modify patient information helps prevent breaches and insider threats.
Regular employee training and awareness programs are indispensable in maintaining HIPAA cyber security standards. Educating staff on best practices, such as recognizing phishing attempts and using secure passwords, strengthens the organization’s overall security posture. By prioritizing these key components, healthcare entities can uphold their commitment to keeping patient data safe and confidential.
Compliance Requirements for Organizations
Ensuring compliance with HIPAA regulations is a top priority for healthcare organizations. Organizations must implement strict security measures to safeguard patient information and meet the requirements. This includes conducting regular risk assessments to identify vulnerabilities in their systems and networks.
Organizations are also required to provide ongoing employee training on data security practices and protocols. All staff members must understand the importance of protecting sensitive data and how to handle it properly.
Maintaining detailed documentation of policies and procedures related to data protection is crucial for demonstrating compliance during audits or investigations. Additionally, organizations must appoint a designated security officer to oversee HIPAA compliance efforts.
Regular monitoring of systems and networks is necessary to detect any unauthorized access or breaches promptly. Organizations must also have incident response plans to address security breaches effectively when they occur.
Common Cybersecurity Threats in the Healthcare Industry
The healthcare industry faces numerous cybersecurity threats that put sensitive patient data at risk. One common threat is ransomware attacks, where hackers encrypt data and demand a ransom for release. These attacks can disrupt patient care and compromise medical records.
Phishing scams are another prevalent threat in the healthcare sector. Cybercriminals send deceptive emails to employees, tricking them into disclosing confidential information or downloading malware onto hospital systems. This can lead to data breaches and financial losses for organizations.
Additionally, insider threats pose a significant risk to healthcare cybersecurity. Employees with access to sensitive data may intentionally or unintentionally misuse it, resulting in unauthorized disclosures or manipulations of patient information.
Common Cybersecurity Threats in the Healthcare Industry
To combat these threats, healthcare organizations must implement robust security measures such as regular employee training on cybersecurity best practices, strong password policies, multi-factor authentication, and encryption protocols to safeguard patient data from potential breaches.
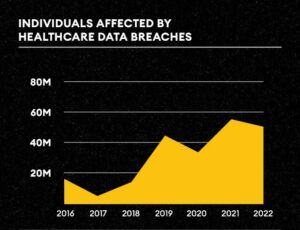
Millions of individuals affected by healthcare data breaches feel vulnerable and exposed. These breaches compromise personal information such as medical history and insurance details and erode trust in the healthcare system. The repercussions of having one’s sensitive data exposed can be far-reaching, leading to identity theft, financial loss, and even emotional distress. Victims often find themselves navigating through a maze of paperwork and phone calls as they try to rectify the damage caused by these breaches. Moreover, the fear of future attacks looms large, causing anxiety and mistrust in an already complex healthcare landscape. As data breaches continue to rise, organizations must prioritize cybersecurity measures to safeguard the privacy and security of their patients’ information.
Best Practices for Maintaining HIPAA Compliance
HIPAA compliance is crucial for safeguarding sensitive patient information in the healthcare industry. To maintain compliance, organizations should start by conducting regular risk assessments to identify potential vulnerabilities in their systems and processes. Robust access controls and encryption measures can help protect data at rest and in transit.
Training all employees on HIPAA regulations and best practices is essential to creating a culture of compliance within the organization. Regularly monitoring network activity and auditing user access can help detect unauthorized breaches or suspicious behavior promptly. Establishing clear policies for data retention, disposal, and incident response protocols is key to addressing security incidents effectively.
Regularly updating software patches and staying informed about emerging cybersecurity threats are critical to maintaining HIPAA compliance. Collaborating with IT security experts can provide valuable insights into implementing advanced security measures tailored to the organization’s specific needs. By prioritizing these best practices, healthcare entities can ensure ongoing adherence to HIPAA regulations while mitigating potential risks associated with cyber threats.
Conclusion
Ensuring compliance with HIPAA regulations is crucial for the healthcare industry to safeguard patient information and maintain trust. Cybersecurity threats continue evolving, so organizations must stay vigilant and implement best practices to protect sensitive data. By understanding the critical components of HIPAA cybersecurity and adhering to compliance requirements, healthcare entities can mitigate risks and enhance their overall security posture. Prioritizing HIPAA in cybersecurity helps organizations meet regulatory standards and demonstrates a commitment to upholding patient privacy in an increasingly digital world.
