The HIPAA Security Rule is a critical part of the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, designed to protect electronic protected health information (ePHI). Every covered entity and business associate must have policies in place that align with its requirements.
This article will explain what the HIPAA Security Rule requires and the essential elements your policies must include to ensure compliance.
Understanding the HIPAA Security Rule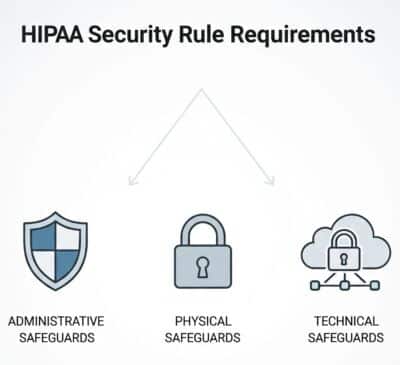
The HIPAA Security Rule sets national standards for protecting ePHI that is created, received, maintained, or transmitted electronically.
Its primary goals are to:
-
Maintain the confidentiality of patient data
-
Ensure the integrity of information
-
Guarantee the availability of data when needed
Key Safeguards Required by the HIPAA Security Rule
The Security Rule is built around three safeguard categories:
1. Administrative Safeguards
Your policies must cover:
-
Security Management Process – Risk analysis, risk management, and incident response plans
-
Workforce Security – Ensuring only authorized staff have ePHI access
-
Security Awareness Training – Ongoing staff education on threats and best practices
-
Contingency Planning – Data backup, disaster recovery, and emergency operations plans
2. Physical Safeguards
Your policies should include:
-
Facility Access Controls – Restricting physical access to servers and data centers
-
Workstation Security – Guidelines for secure workstation use and location
-
Device & Media Controls – Secure disposal, reuse, and movement of devices containing ePHI
3. Technical Safeguards
Your policies must address:
-
Access Control – Unique user IDs, automatic logoff, and emergency access
-
Audit Controls – System activity logs and monitoring
-
Integrity Controls – Measures to prevent ePHI alteration or destruction
-
Transmission Security – Encryption for data in transit
Documentation & Review Requirements
Under HIPAA, your organization must:
-
Maintain written policies and procedures for all safeguards
-
Review and update them regularly to reflect new risks
-
Document all updates and training sessions
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Failing to meet HIPAA Security Rule requirements can lead to:
-
Civil fines up to $1.9 million per year for willful neglect
-
Criminal penalties for intentional violations
-
Loss of patient trust and reputational harm
Final Thoughts
Your HIPAA Security Rule compliance depends on detailed, well-enforced policies that cover all administrative, physical, and technical safeguards. Regular updates, risk assessments, and employee training will keep your organization secure and compliant.
