The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is a crucial regulation for any organization that handles protected health information (PHI). While many know about the need for HIPAA compliance, creating effective HIPAA security policies can seem like a daunting task. These policies are not just a legal requirement; they are the foundation of your organization’s security posture. They protect patient data, build trust, and prevent costly data breaches.
This guide breaks down the essential steps to help you develop robust and effective HIPAA security policies that protect your organization and your patients.
1. Understand the HIPAA Security Rule
The first step is to get a firm grasp of the HIPAA Security Rule. This rule sets the standards for protecting PHI in electronic form (ePHI). It is divided into three main safeguards:
- Administrative Safeguards: These are the administrative actions, policies, and procedures to manage the selection, development, implementation, and maintenance of security measures. This includes a risk analysis, risk management plan, and employee training.
- Physical Safeguards: These cover the physical protection of electronic information systems, equipment, and the facility itself from unauthorized access. This includes policies for facility access control and workstation security.
- Technical Safeguards: These are the technology and the policy and procedures for using it to protect ePHI and control access to it. This includes access control, audit controls, and data encryption.
Your policies must address each of these safeguard categories comprehensively.
2. Conduct a Thorough Risk Analysis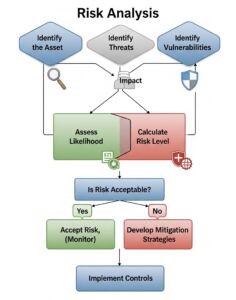
Before you can write policies, you need to know what you’re protecting against. A risk analysis is a required and critical step. It involves identifying potential threats and vulnerabilities to your ePHI.
How to conduct a risk analysis:
- Identify where PHI is stored, received, maintained, or transmitted. This includes servers, computers, laptops, mobile devices, and third-party services like cloud storage.
- Identify and document potential threats and vulnerabilities. Threats could be anything from a natural disaster to a malicious cyber-attack. Vulnerabilities might include a lack of employee training or outdated software.
- Assess the potential impact of these threats. How would a data breach affect your organization? What is the likelihood of it happening?
- Prioritize risks. Focus on the most significant risks first to develop a remediation plan.
The findings from your risk analysis will directly inform the content of your security policies.
3. Develop Specific, Actionable Policies
Once you’ve identified your risks, you can start writing your policies. Your policies should be clear, specific, and actionable. Avoid vague language. For example, instead of “Employees should be careful with patient data,” a policy should state, “All employees must use a strong, unique password and enable two-factor authentication on all systems containing ePHI.”
Key policies to develop:
- Information System Access Policy: This policy dictates who can access ePHI and under what conditions. It should include procedures for granting, revoking, and managing user access.
- Password Policy: Detail requirements for password strength, complexity, and change frequency.
- Device and Media Control Policy: This policy should cover the secure use and disposal of devices that store ePHI, such as hard drives, USB drives, and laptops.
- Incident Response Plan: A crucial policy that outlines the steps to take in the event of a security breach or incident. It should include who to contact, how to contain the breach, and how to notify affected individuals and authorities.
- Employee Training Policy: This policy ensures all staff are regularly trained on HIPAA regulations and your organization’s security policies.
4. Implement and Enforce the Policies
A policy is only effective if it’s followed. Implementation and enforcement are just as important as the writing process.
- Communicate Clearly: Ensure all employees receive and understand the new policies.
- Provide Training: Regular training sessions are a must. Use real-world examples to make the training relatable and effective.
- Appoint a HIPAA Security Officer: This individual is responsible for overseeing the development, implementation, and enforcement of security policies.
- Conduct Regular Audits: Periodically review your policies and procedures to ensure they are being followed. This also helps you identify any new vulnerabilities.
5. Review and Update Policies Regularly
The threat landscape is constantly evolving, and so are technologies. Your HIPAA security policies should not be static documents. They must be reviewed and updated at least annually or whenever there’s a significant change in your organization’s technology or business operations. This ensures your policies remain relevant and effective against new threats.
By following these steps, you can move from a state of uncertainty to having a clear, actionable set of policies that not only comply with HIPAA but also genuinely protect your organization and the sensitive data you manage. Investing in effective security policies is an investment in your patients’ privacy and your organization’s future.
Ready to secure your organization’s data?
Contact us today for a free consultation and let our experts help you develop and implement a comprehensive HIPAA compliance plan tailored to your needs.
