Free Phishing email Campaign Simulation Solution with Online Security Awareness Training and Dark Web Monitoring Tool
Learn how to avoid Phishing attacks by using anti-Phishing Simulator tests for employees, security awareness training, dark web monitoring, policy implementation, and technical safeguards. The objective is to prevent and detect hacking and ransomware attacks. Use our free Phishing simulator tool to get started today.
FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center has said that the number of Social Engineering attacks will increase on USA companies and individuals.
What is a Phishing Attack on Employees?
Phishing is a type of social engineering attack used to steal user data, including login credentials and credit card numbers. Hackers and cybercriminals target the employees and they take advantage of your trust, panic, greed, fear, and human error.
What are the different types of Phishing Attacks?
- Spear Phishing – Spear phishing is an email or electronic communications scam targeted towards a specific individual, organization or business. Although often intended to steal data for malicious purposes, cybercriminals may also intend to install malware on a targeted user’s computer.
- Vishing – Means voice phishing. It is the fraudulent practice of making phone calls or leaving voice messages purporting to be from reputable companies in order to induce individuals to reveal personal information. Vishing banking scams are a type of attack that involves a call from someone who says they’re from your bank or some other financial organization or government Tax authorities.
- SMiSHing – It is just the SMS version of phishing scams. Instead of a scammy email, you get a scammy-sounding text message on your smartphone.
- Dropbox Phishing – Dropbox, a file-sharing platform is interesting to scammers looking for personal information. A Dropbox phishing attack uses an email that appears to be from the website and prompts the victim to log in.
- Google Docs Phishing – Google Docs phishers spoof a legitimate-looking log-in prompt to trick their victims into handing over their passwords.
- Image Phishing – If you are receiving emails containing images according to your interest, then BEWARE! It could be a phishing attack.
- Deceptive Phishing – Deceptive phishing is by far the most common type of phishing attack in which scammers attempt to replicate a legitimate company’s email correspondence and prompt victims into handing over information or credentials.
- Whaling / CEO Fraud – This technique targets C-suite posts like CEO, CFO, COO – or any other senior management positions – who are considered to be big players in the information chain of any organization, commonly known as “whales” in phishing terms. When the CEO or the head of a department asks for some files, most people wouldn’t question it, even if it’s an odd request.
- W2 Phishing – This is a cyber tactic that hackers use to send a fake email from the accounting/finance department. Their aim is to acquire employees’ sensitive information from W-2s so they can leverage it to commit identity fraud.
- Search Engine Phishing – Search engine phishing occurs through online website search engines. A user encounters offers or messages that entice the person to visit the website. The search process itself may be legitimate, but the website is actually fake and only exists to steal the person’s personal information.
- Pharming – It is a scamming practice in which malicious code is installed on a personal computer or server, misdirecting users to fraudulent Web sites without their knowledge or consent.
Solution for Anti-Phishing Test for Employees
Our tools provide the combined solution by using the following approach.
Simulated Phishing Exercises
- At least one phishing simulation will be launched every six months in order to test the impact of the training and to identify any high-risk users.
- Instant follow-up training will be deployed to any employees who compromise their credentials during a phishing simulation in order to reduce risk as soon as possible.
Security Awareness Training
- Analyze each users’ current security strengths and weaknesses using a Gap Analysis Quiz.
- Using the results of the quiz, each employee will receive a new security awareness course every four weeks, with courses being prioritized to address their weakest areas first.
- Custom compliance courses will also be delivered periodically.
Dark Web Monitoring
Ongoing dark web monitoring will take place in order to identify and avoid early-stage attacks that leverage stolen employee credentials, like compromised usernames and passwords.
The Objective of the Anti-Phishing Simulator Tool for Employees
- Identify which employees are at high risk of being compromised in a phishing attack
- Obtain an ongoing view of which employees are vulnerable to phishing attacks
- Reduce the likelihood of users falling victim to future phishing attacks
- Develop a security-minded culture in your organization
Key features
- Automated phishing: The system can deploy regular phishing simulations – allowing you to assess user performance over time.
- Realistic template library: Library of phishing emails and landing pages impersonating trusted organizations, banks, and more.
- Custom emails and landing pages: Crafted simulated phishing campaigns, impersonate internal communications, and more.
- Inline training: Automatically send out additional training content to users who become compromised in phishing simulations.
- Real-time tracking: See how users interact with simulations in real-time, giving key insight into how users will perform during a real attack.
- In-depth reporting: View the individual performance of users or assess your organization in departments or as a whole – with custom reporting.
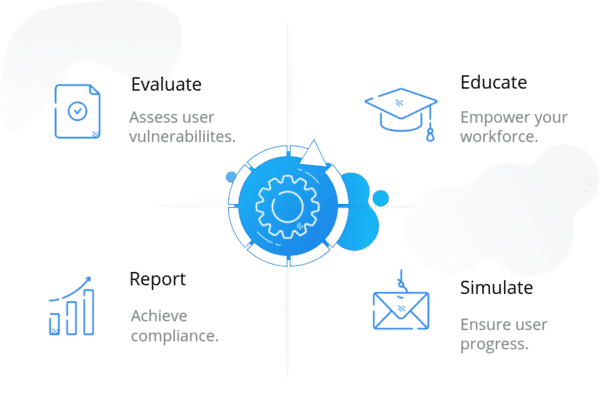
How the System Works
Evaluate – Educate – Simulate – Report
Users will receive a bespoke security awareness training program unique to individuals’ infosec vulnerabilities – with the option of deploying phishing simulations to provide practical risk assessments.
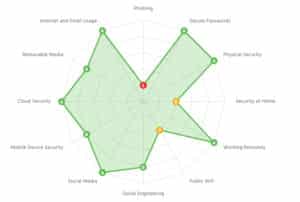
1. Evaluate – Determine users’ risk profile
To start off, the system conducts an initial risk assessment on users to determine their individual knowledge gaps. We call this the gap analysis questionnaire.
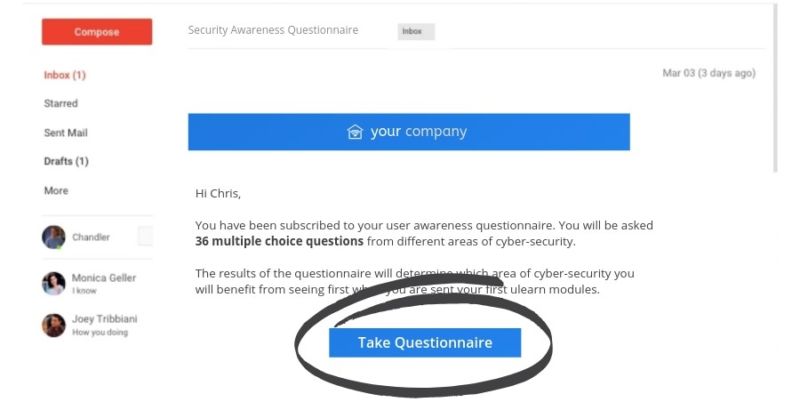
Here’s how the gap analysis questionnaire works:
- Invitation: Users will receive an email invitation to their questionnaire, which they can start at a time convenient for them.
- Assessment: Once started, users will be quizzed on 12-core areas of infosec best practice, with this multiple-choice assessment lasting approx. 10 minutes.
- Course enrolment: Using the results from the gap analysis stage, the system will automatically craft a 12-month training program unique to each user – with weaker subjects (e.g., phishing, passwords etc.), being deployed first.
2. Educate – Empower your users
Now users’ programs have been created, the system will automatically enroll each user onto their first course.
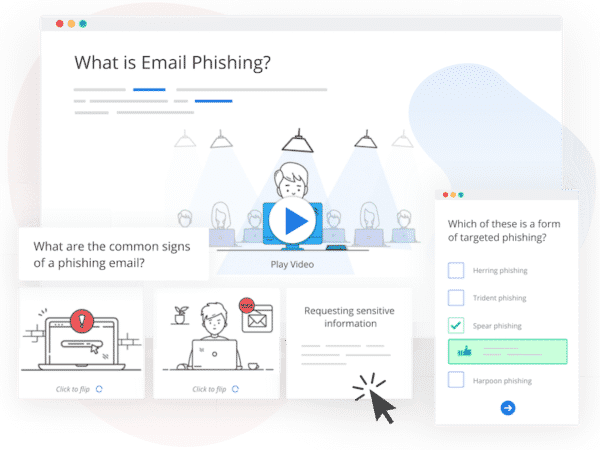
Here’s a quick overview of your users’ 12-month training program:
- Prioritized courses: Users will receive courses that match their weakest areas first (e.g., user scored weakest in ‘phishing’ during the gap analysis stage. Therefore, their first course will be ‘Phishing Awareness for Beginners’)
- Automated invitations and reminders: To keep your training continuous, efficient, and admin-lite, the system will send automatic course invitations to your users, as well as reminders for outstanding courses.
- Regular bite-sized courses: Users will be educated on various infosec and compliance best practices, with deploying one bite-sized course per month (this frequency can be customized by the admin).
- Engaging & jargon-free content: Courses come with video, interactive and blog-style content to engage different styles of learning whilst avoiding confusing tech jargon.
3. Simulate – Test users’ learning progress
To ensure users have improved their security behavior, we launch targeted simulated phishing tests.
Here’s how you can assess user vulnerability
- Realistic phishing templates: The ever-growing library of phishing templates come with pre-made emails and landing pages, replicating trusted organizations and services.
- Custom-built templates: Create your own custom phishing templates, useful for targeted campaigns that impersonate internal communications.
- Automated simulations: Send regular phishing campaigns to ensure user progress over time, with fully automated campaigns.
- Real-time tracking: Track real-time opened, clicked, and compromised rates of users to determine how they would react to a real-life attack.
- Granular reporting: Develop a clear risk profile of your organization and individual users by digging deep into in-depth reporting metrics.
4. Report: Aid your efforts in regulatory compliance
As your users progress through their training courses, you’ll be able to view key insights of your organization’s performance straight from the data-driven dashboard.
List of Courses
Beginner
- Phishing
- Public Wi-Fi
- Secure Passwords & Authentication
- Physical Security
- Cloud Security
- Internet & Email Use
- Mobile Device Security
- Removable Media
- Social Engineering
- Using Social Media Safely
- Working Remotely
- Security at Home
Intermediate
- Ransomware
- What Makes a Cyber Criminal?
- The Internet of Things
- The Insider Threat
- Information & Data
- Smishing
- Internet & Email Use +
- Phishing +
- Data Loss
- Denial of Service Attacks (DOS)
- Patching & Updating
- Vishing
Advanced
- Spyware & Adware
- The Dark Web
- Protecting Your Online Privacy
- BYOD
- Phishing ++
- File Sharing in the Workplace
- 10 Steps to Secure Your Home Network
- Clear Desk Policy
- Online Payments
- Malicious Websites & Applications
- Malware
- Using Third-Party Services Securely
Dark Web Monitoring – Proactive Employee Data Monitoring
What is Dark Web Monitoring?
Dark Web Monitoring enables to quickly identify exposed employee email accounts and identities that have been publicly disclosed online via third-party data breaches.
With billions of credentials present in data dumps, paste sites, and hacking forums, employees that sign up to third-party services with their work email address could be leaving your organization at huge risk of social engineering, business email compromise (BEC), and other damaging attacks.
With Dark Web Monitoring, you can:
- Identify exposed employee accounts: Dark Web Monitoring identifies accounts that are exposed on paste sites, data dumps, and hacking forums
- Locate what employee data is exposed: Common data includes email addresses, passwords, usernames, etc.
- Help prevent data loss: Locating these at-risk accounts enables you to safeguard users from social engineering and BEC attacks
- Obtain actionable steps: Enables follow-up user training on security best practice
How Dark Web Monitoring works
- Step One: Conducts a deep web search through data dumps, paste sites, and hacking forums
- Step Two: Identifies users that have had account information exposed online
- Step Three: Collates your users’ results into an easy-to-digest format, accessible from your account dashboard
Dark Web Monitoring key features
- Quick web search enables you to rapidly identify exposed accounts
- Gathers high-level data (i.e., number of exposed accounts & source of breach) neatly into your dashboard
- View each user’s exposed data breakdown from their profile within the tool
- 100% free with your subscription
What the different types of data on Dark Web Monitoring mean to your organization’s security
Email addresses
These will be present in every breach that is visible on Dark Web Monitoring, as your users’ emails are used to find their exposed credentials. An attacker having the email address of one of your users is not generally a risk in itself, as this is likely to be public information anyway.
Passwords
If a user has had their password exposed in a breach, it is likely to be a major cause of concern. If the password has been cracked, it will have allowed an attacker to access the user’s account on the service on which the breach happened. More importantly for you, however, is that a very high proportion of people reuse their passwords across online services. This means that your user could be using that same password to protect their company email account or any of their other business logins, causing a risk to your business network.
IP addresses
IP addresses – the unique numbers associated with every device that connects to the internet – sometimes appear in breaches. This will happen when a service stores the IP addresses that its users log in from. Knowing your company’s IP addresses could help an attacker launch an attack such as DDOS, but as IP addresses are fairly easy to harvest, having them exposed in breaches does not necessarily cause a significantly heightened risk to your organization.
Personal details including birthdays, job titles etc.
Any personal details that are exposed in breaches cause a heightened risk of phishing and social engineering. An attacker could use information like one of your users’ birthdays in order to help them pretend to be someone within the organization. Exposed personal information also causes a high stolen identity risk, allowing an attacker to bypass security protections to access the users’ accounts.
Protecting your organization
If you notice that one of your user’s passwords has been exposed in a breach, this creates an immediate risk to you and your user due to the chance of them reusing passwords. To protect your organization and your user, you should ensure that they change their passwords and do not reuse them in the future.
Any other type of information that is exposed about your users will increase the risk of phishing. If any of your users have had personal information exposed in breaches, they should be alert about anyone trying to access their accounts with their stolen identity. All your other users should also be alerted about the risk of an attacker using the exposed information to pose as the user in an attempt to infiltrate your organization’s network.

You will be able to see the services from which the user’s data has been exposed, the date when the breach happened, the date when the breach was added to our database, and the type of information that was exposed.
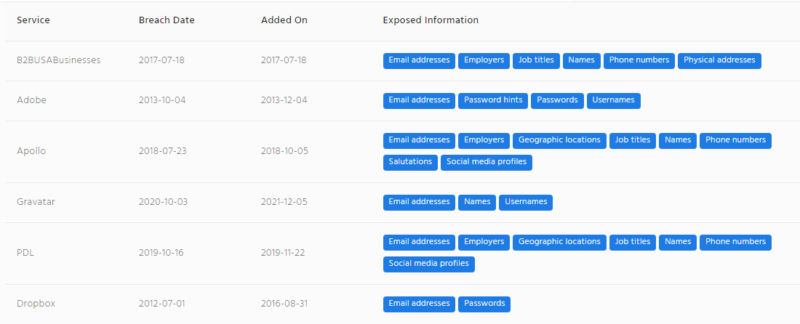
Get started today by using our tool for free for 14 days. Contact us at Bob@hipaatraining.net to get started today. We have clients in USA, UK, Canada, Asia, Australia, France, Saudi Arabia, and many other countries who use our services.
Stay Proactive in your Cybersecurity projects.
